Ranchos of California
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Spanish and, later, Mexican governments encouraged settlement of territory now known as California by the establishment of large land grants called ranchos, from which the English word ranch is derived. Land-grant titles (concessions) were government-issued, permanent, unencumbered property-ownership rights to land called ranchos. Devoted to raising cattle and sheep, the owners of the ranchos attempted to pattern themselves after the landed gentry of Spain. Their workers included Californian Native Americans who had learned to speak Spanish, many of them former Mission residents. Of the 800-plus grants, Spain made about 30 between 1784 and 1821. The remainders were granted by Mexico between 1833 and 1846. The ranchos established land-use patterns that are recognizable in the California of today. Rancho boundaries became the basis for California's land survey system, and can still be found on modern maps and land titles. Ranchos were partially based on geography, such as access to river water. Land development in the 20th and 21st century often follow the boundaries of the ranchos, and often retain the original name. For example, "Rancho San Diego," an unincorporated 'rural-burb' east of San Diego, or "Rancho Bernardo,", a master plan suburb in the city of San Diego.
Contents
- 1 Spanish era
- 2 Mexican era
- 3 American era
- 4 List of Ranchos of California
- 5 See also
- 6 Notes and references
- 7 Further reading
- 8 External links
Spanish era
During Spanish rule (1769–1821), the ranchos were concessions from the Spanish crown, permitting settlement and granting grazing rights on specific tracts of land, while the crown retained the title. The ranchos, that is, the settlement by individuals of tracts of land outside presidio, mission, and pueblo boundaries, began in 1784, when Juan Jose Dominguez got permission from Spanish Governor Pedro Fages to put his cattle on the 48,000-acre (190 km2) Rancho San Pedro.[1] The land concessions were usually measured in leagues. A league of land would encompass a square that is one Spanish league on each side – approximately 4,428 acres (18 km2).
List of Spanish era concessions
(Listed chronologically by date of concession)
|
Concession |
Date |
Grantor |
Grantee |
Size |
Location |
County |
|
1784 |
48,000 acres (194 km2) |
San Pedro, Torrance, Redondo Beach, Hermosa Beach, Manhattan Beach, Lomita, Gardena, Harbor City, Wilmington, Carson, Compton |
||||
|
1784 |
167,000 acres (676 km2) |
Long Beach, Lakewood, Downey, Norwalk, Santa Fe Springs, Whittier, Fullerton, Huntington Beach, Seal Beach, Anaheim, Buena Park, Garden Grove, Artesia, Cerritos |
Orange and Los Angeles |
|||
|
1784 |
36,403 acres (147 km2) |
Atwater Village, Eagle Rock, Glassell Park, Glendale, Highland Park |
||||
|
1794 |
26,529 acres (107 km2) |
|||||
|
1795 |
Jose Vicente Feliz |
6,647 acres (27 km2) |
||||
|
1795 |
Patrico, Miguel, and Francisco Javier Pico |
113,009 acres (457 km2) |
||||
|
1795 |
Jose Maria Soberanes & Joaquin Castro |
8,446 acres (34 km2) |
||||
|
1795 |
Antonio Aceves and Antonio Romero |
17,712 acres (72 km2) |
||||
|
1795 |
35,000 acres (142 km2) |
San Mateo, Belmont, San Carlos, Redwood City, Atherton, Menlo Park |
||||
|
1802 |
Miguel Ortega |
17,760 acres (72 km2) |
||||
|
1802 |
Ygnacio Rodriguez and Jose Polanco |
48,672 acres (197 km2) |
Newbury Park, Thousand Oaks, Lake Sherwood, Westlake Village, Oak Park |
|||
|
1802 |
13,300 acres (54 km2) |
|||||
|
1803 |
Mariano Castro |
24,066 acres (97 km2) |
||||
|
1809 |
31,629 acres (128 km2) |
Part of Rancho San Pedro |
||||
|
1809 |
Ygnacio Ortega |
13,066 acres (53 km2) |
||||
|
1810 |
29,513 acres (119 km2) |
Bell, Bell Gardens, Commerce, Cudahy, East Los Angeles, Lynwood, Montebello, South Gate, Vernon |
||||
|
1810 |
José Antonio Yorba & Juan Pablo Peralta (Nephew) |
63,414 acres (257 km2) |
Santa Ana, El Modena, Orange, Irvine, Costa Mesa, Tustin, Olive. |
|||
|
1819 |
Machado and Talamantes families |
13,920 acres (56 km2) |
Culver City, Inglewood, Marina del Rey, Palms, Playa del Rey, Santa Monica (Ocean Park Dist), Venice |
|||
|
1820 |
44,800 acres (181 km2) |
Albany, Alameda, Berkeley, Emeryville, Oakland, Piedmont, San Leandro |
||||
|
1821 |
Bernardo Higuera and Cornelio Lopez |
3,127 acres (13 km2) |
||||
|
1821 |
Antonio Maria Castro |
4,310 acres (17 km2) |
||||
|
1821 |
José Higuera |
4,394 acres (18 km2) |
Mexican era
See also: List of Ranchos of California
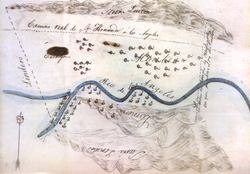
Sketch map or diseño of Rancho Providencia, 1840s.
It was not until the Mexican era (1821–1846) that the titles to the plots of land were granted to individuals. In 1821, Mexico achieved its independence from Spain, and California came under control of the Mexican government. The 1824 Mexican Colony Law established rules for petitioning for land grants in California; and by 1828, the rules for establishing land grants were codified in the Mexican Reglamento (Regulation). The Acts sought to break the land monopoly of the missions and also paved the way for luring additional settlers to California by making land grants easier to obtain. The procedure included a 'diseño' – a hand-drawn topological map - to define the area.[2] The Mexican Governors of Alta California gained the power to grant state lands, and many of the Spanish concessions were subsequently patented under Mexican law—frequently to local "friends" of the governor.
Through the Secularization Act of 1833, the Mexican government repossessed most of the lands initially "granted" to the Franciscan missions (about 1,000,000 acres (400,000 ha) per mission) by the Spanish crown who had "appropriated" the land "for the Mission Indians".[3][4] Secularization was implemented between 1834 and 1836. The Mexican government allowed the padres to keep only the church, priest's quarters and priest's garden. The army troops guarding each Mission were dismissed. A commissioner would oversee the mission's crops and herds, while the land was divided up as communal pasture, a town plot, and individual plots for each Indian family. The Mission Indians without the discipline supplied by the Franciscan friars and the troops assigned to each mission usually soon abandoned their fields (if granted) and joined other interior tribes or sought work on the new ranchos and expanding pueblos.
The number of Mexican land grants greatly increased after the secularization of the missions in 1834. Although the original intent of the secularization legislation was to have the property divided among former surviving Mission Indians, most of the grants were made to local Californios.(See: List of Ranchos of California)
The Mexican rancho grants were provisional. The boundaries, on paper, had to be "officially" surveyed and marked. Since there were very few surveyors this requirement was seldom met. The grantee could not initially subdivide or rent out the land. The land had to be used for grazing or cultivated. Some kind of residential house had to be built within a year—most were initially simple adobe walled cabins. Public roads crossing through the property could not be closed. Most rancho grants boundaries and other requirements were not checked by the poorly paid and organized "government" of California who had little interest in land that brought in no taxes—money to run the government came from tariffs collected at Monterey, California.
American era
The United States (US) declared war against Mexico on May 13, 1846. Action in California began with the Bear Flag Revolt on June 15, 1846. On July 7, 1846, US forces took possession of Monterey, the capital of California, and terminated the authority and jurisdiction of Mexican officials that day.[5] Armed resistance ended in California with the Treaty of Cahuenga signed on January 13, 1847. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, ending the war, was signed February 2, 1848 and California became a Territory of the United States. Between 1847–1849, California was run by the U.S. military. A constitutional convention met in Monterey in September 1849, and set up a state government. It operated for 10 months before California was admitted to the Union as the 31st State by Congress, as part of the Compromise of 1850, enacted on September 9, 1850.
California Gold Rush
While the end of the 1840s saw the close of Mexican control over Alta California, this period also marked the beginning of the rancheros’ greatest prosperity. Cattle had been raised primarily for their hides and for the tallow, as there was no market for large quantities of beef. This dramatically changed with the onset of the Gold Rush, as thousands of miners and other fortune seekers flooded into northern California. These newcomers needed meat, and cattle prices soared with demand. The rancheros enjoyed the halcyon days of Hispanic California.[6]
Land claims
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the Mexican land grants would be honored. In order to investigate and confirm titles in California, American officials acquired the provincial records of the Spanish and Mexican governments in Monterey.[7][8]
Sponsored by California Senator William M. Gwin, in 1851 the United States Congress passed "An Act to Ascertain and Settle Private Land Claims in the State of California". The Act required all holders of Spanish and Mexican land grants to present their titles for confirmation before the Board of California Land Commissioners.[9] Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, this Act placed the burden of proof of title on landholders.[10] In many cases, the land grants had been made without clearly defining the exact boundaries. Even in cases where the boundaries were more specific, many markers had been destroyed before accurate surveys could be made. Aside from indefinite survey lines, the Land Commission had to determine whether the grantees had fulfilled the requirements of the Mexican colonization laws. While the Land Commission confirmed 604 of the 813 claims it reviewed, most decisions were appealed to US District Court and some to the Supreme Court.[11] The confirmation process required lawyers, translators, and surveyors, and took an average of 17 years (with American Civil War, 1861–1865) to resolve. It proved expensive for landholders to defend their titles through the court system. In many cases, they had to sell their land to pay for defense fees or gave attorneys land in lieu of payment.[12][13]
Land from titles not confirmed became part of the public domain, and available for homesteaders, who could claim up to 160-acre (0.65 km2) plots in accordance with federal homestead law. Rejected land claims resulted in claimants, squatters, and settlers pressing Congress to change the rules. Under the Pre-emption Act of 1841, owners were able to "pre-empt" their portions of the grant, and acquire title for $1.25 an acre up to a maximum of 160 acres (0.65 km2). Beginning with Rancho Suscol in 1863, special acts of Congress were passed that allowed certain claimants to pre-empt their land – without regard to acreage. By 1866 this privilege was extended to all owners of rejected claims.[14][15]
Disintegration
The rancheros became land rich and cash poor, and the burden of attempting to defend their claims was often financially overwhelming. Grantees lost their lands as a result of mortgage default, payment of attorney fees, or payment of other personal debts. Land was also lost as a result of fraud. A sharp decline in cattle prices, the floods of 1861–1862, and droughts of 1863–1864, also forced many of the overextended rancheros to sell their properties to Americans. They often quickly subdivided the land and sold it to new settlers, who began farming individual plots.[16]
A shift in the economic dominance of grain farming over cattle raising was marked by the passage of the California "No-Fence Law" in 1874. This repealed the Trespass Act of 1850, which had required farmers to protect their planted fields from free-ranging cattle. The repeal of the Trespass Act required that ranchers fence stock in, rather than farmers fencing cattle out. The ranchers were faced with either the high expense of fencing large grazing tracts or selling their cattle at ruinous prices.[17][18]
Legacy
The ranchos established land-use patterns that are still recognizable in contemporary California.[19] Many communities still retain their Spanish rancho name. For example, Rancho Penasquitos, the first land grant by the Spanish in today's San Diego County, is now a suburb with in the city of San Diego. Modern communities often follow the original boundaries of the rancho, based on geographic features and abstract straight lines. Today, most of the original rancho land grants have been dismantled and sold off to become suburbs and rural-burbs. A very small number of ranchos are still owned by descendants of the original owners, retain their original size, or remain undeveloped.
List of Ranchos of California
Main article: List of Ranchos of California
See also
- California hide trade
- History of California through 1899
- Spanish missions in California
- United States Court of Private Land Claims
Notes and references
1. Jump up ^ Robinson, William Wilcox (1979). Land in California. Ayer Co. ISBN 978-0-405-11352-9.
2. Jump up ^ Cleland, Robert, 1975, The Cattle on a Thousand Hills: Southern California, 1850–1880, The Huntington Library, San Marino, CA.
3. Jump up ^ Secularization Of The Missions
4. Jump up ^ Davis, William Heath. (1929) Seventy-five Years in San Francisco – Missions and their Wealth; Hacendados and Their Property
5. Jump up ^ More v. Steinbach, U.S. Supreme Court, 127 U.S. 70 (1888)
6. Jump up ^ "The California Cattle Boom, 1849–1862"
7. Jump up ^ Beck, Warren A. and Ynez D. Haase, Historical Atlas of California, first edition, p. 24
8. Jump up ^ "Spanish and Mexican Land Grant Maps, 1855–1875", California State Archives
9. Jump up ^ Paul W Gates, 1971, The California Land Act of 1851, California Historical Society, Vol. 50, No. 4 (Dec., 1971), pp. 395–430
10. Jump up ^ "Ranchos of California": Extracts from Cris Perez, Grants of Land in California Made by Spanish or Mexican Authorities
11. Jump up ^ Report of the Surveyor General 1844–1886
12. Jump up ^ "Adjudication of Private Land Claims in California, circa 1852–1892"
13. Jump up ^ Ranchos and the Politics of Land Claims
14. Jump up ^ Paul W Gates, 2002,Land and Law in California: Essays on Land Policies, Purdue University Press, ISBN 978-1-55753-273-2
15. Jump up ^ Gordon Morris Bakken, 2000, Law in the western United States, University of Oklahoma Press, ISBN 978-0-8061-3215-0
16. Jump up ^ Leonard Pitt, Ramon A. Gutierrez, 1999,Decline of the Californios: A Social History of the Spanish-Speaking Californias, 1846–1890, University of California Press,ISBN 978-0-520-21958-8
17. Jump up ^ Ludeke, John. "The No Fence Law of 1874: Victory for San Joaquin Valley Farmers," California History 59, no. 2 (1980): 98–115.
18. Jump up ^ "Decimation of the Herds, 1870–1912", San Diego History Journal, January 1965
19. Jump up ^ David Hornbeck, "Land tenure and rancho expansion in Alta California, 1784–1846", Journal of Historical Geography, Volume 4, Issue 4, October 1978, pp. 371–390
Further reading[edit]
- Avina, Rose H. (1976). Spanish and Mexican Land Grants in California, Arno Press, New York.
- Baker, Charles C. (1914). Mexican Land Grants in California, Historical Society of Southern California, Vol IX, pp. 236–243
- Beck, Warren A.; Ynez D. Haase (1974). Historical Atlas of California. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-1212-3. )
- Becker, Robert H. (1969). Designs on the land : disenos of California ranchos and their makers. San Francisco, Book Club of California.
- Beers, Henry Putney (1979). Spanish & Mexican records of the American Southwest : a bibliographical guide to archive and manuscript sources. University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
- Cowan, Robert G. (1956). Ranchos of California. Academy Library Guild, Fresno, Calif.
- Perez, Cris; California State Lands Commission. Grants of Land in California Made by Spanish Or Mexican Authorities. California State Lands Commission. )
- Perez, Crisostomo N. (1996). Land Grants in Alta California. Landmark Enterprises. ISBN 978-0-910845-55-7.
- Hayes, Derek (2007). Historical Atlas of California. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-25258-5.